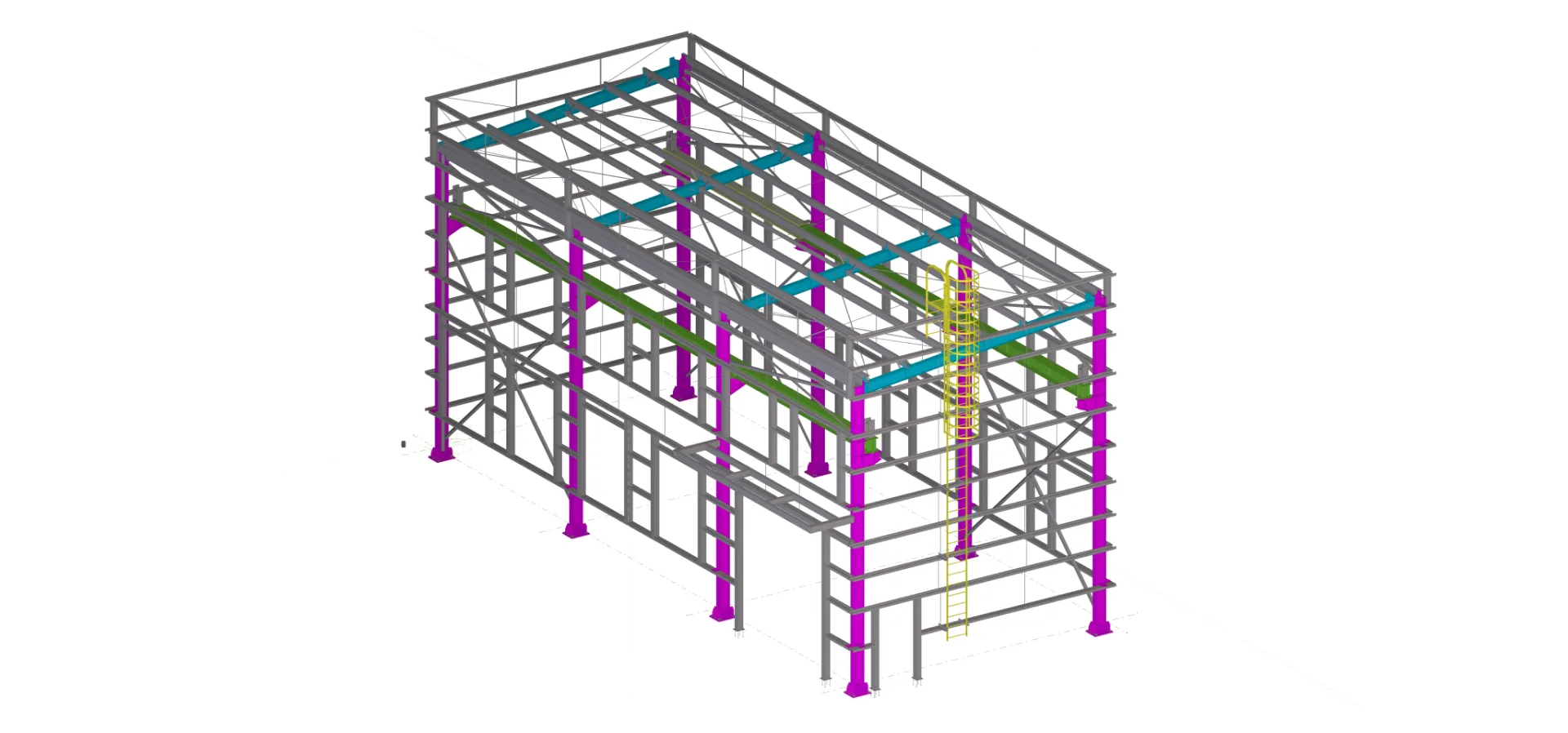
Requirement Analysis: Identify the purpose and requirements for the workshop (e.g., storage, manufacturing, maintenance). This helps in determining the size, design, load-bearing capacity, ventilation, and layout.
Blueprint and Layout Design: Create detailed architectural blueprints and structural designs. This includes:
Floor plans.
Location of columns, beams, doors, and windows.
Electrical and plumbing plans.
Load Calculations and Structural Analysis: Engineers perform structural analysis based on factors like wind load, seismic conditions, snow load, and live and dead loads. Advanced software like STAAD Pro or Tekla Structures is often used.
Material Selection: Choose the grade of steel based on requirements like strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance (e.g., galvanized steel, high-strength low-alloy steel).
Cutting and Welding: Steel components such as beams, columns, trusses, and girders are cut, welded, and fabricated in fabrication shops. CNC machines are used to ensure accuracy.
Prefabrication: Some workshops opt for prefabricated or pre-engineered components to save construction time. These include pre-cut beams, pre-assembled trusses, and pre-made wall panels.
Surface Treatment: Anti-corrosion treatments like galvanizing, powder coating, or painting are applied to fabricated components.
Land Survey and Excavation: Surveying is conducted to prepare the land, followed by excavation for foundation work.
Foundation Construction: Foundations are laid based on the load-bearing capacity and size of the structure. Common types include:
Isolated Footing: Used for individual columns.
Raft Foundation: A continuous slab for large structures.
Pile Foundation: For weak soil conditions.
Foundation Bolts and Anchor Plates: Bolts and anchor plates are installed to ensure a secure connection between the steel columns and the foundation.
Column Erection: Steel columns are lifted and fixed to the foundation using anchor bolts. They serve as the primary load-bearing components.
Beam Placement: Horizontal beams (primary and secondary) are installed, connecting the columns to form the skeleton of the structure. Cranes are usually employed to lift and position the beams.
Roof Truss and Rafter Installation: Roof trusses or rafters are placed to form the skeletal structure of the roof. Purlins are installed horizontally across the trusses.
Bracing and Stiffeners: Cross-bracing and stiffeners are added to provide additional strength and stability against lateral forces like wind and seismic activity.
Roof Panels Installation: Metal roofing sheets (corrugated or standing seam) are laid and securely fastened to the roof purlins.
Wall Cladding: Metal panels, sandwich panels, or insulated panels are fixed to the exterior steel framework for walls. Cladding not only provides protection from the elements but also improves the aesthetics of the building.
Insulation and Ventilation: Depending on the use of the workshop, insulation materials like rock wool or polyurethane can be installed. Skylights or ventilators are also added if required.
Electrical Wiring: Electrical conduits and wires are laid as per the design. This includes lighting, power points, emergency lighting, and control panels.
Plumbing and Drainage: Plumbing lines, water supply, and drainage systems are laid out if required.
Painting and Surface Finish: Final paint coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and give an aesthetic finish. This is essential for steel workshops exposed to moisture or chemicals.
Flooring: Depending on the requirements, the flooring could be concrete, epoxy-coated, or industrial tiles.
Structural Integrity Inspection: Engineers inspect all welds, bolt connections, and critical points to ensure structural integrity.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing, X-ray testing, or magnetic particle inspection may be conducted for weld joints.
Safety Features: Ensure the workshop complies with safety standards and is equipped with fire exits, alarms, and fire extinguishing systems.
Final Walkthrough: Conduct a final inspection of the entire workshop, ensuring compliance with safety regulations, design specifications, and quality standards.
Documentation and Maintenance Guide: Provide the client with all documentation, including as-built drawings, safety manuals, and maintenance schedules.
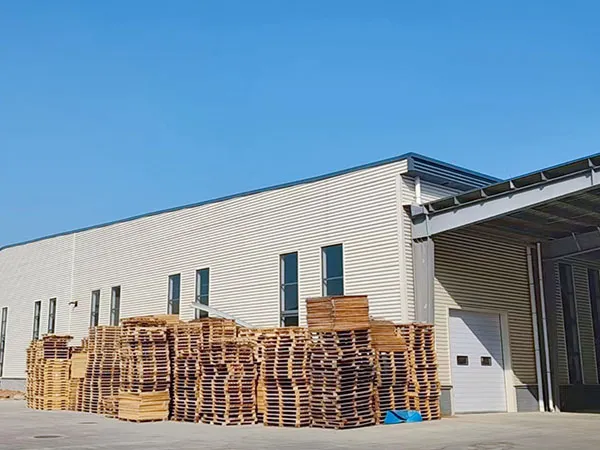

Zhuoyang Chundu Standardized Factory Construction Project
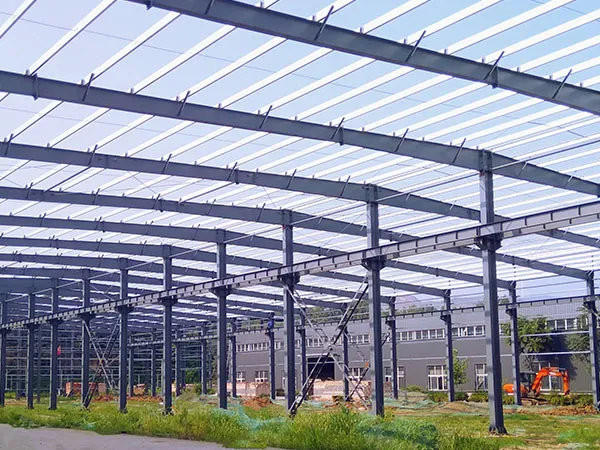

Yiyang Huicheng Steel Structure Factory Construction Project
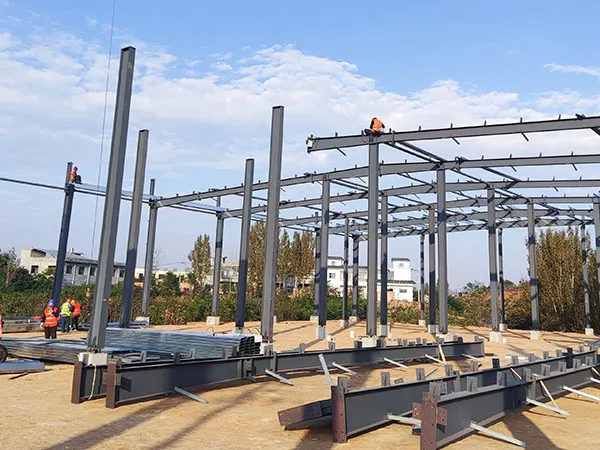

Seed Potato Storage Center Project of Lingshang Selenium Potato Science and Technology Innovation Park in Yaling Town, Yichuan County
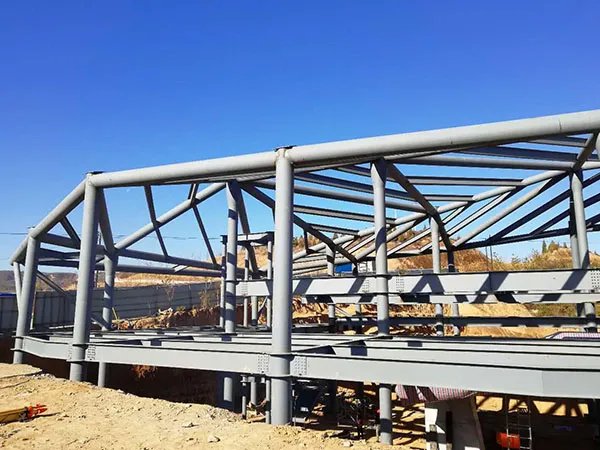

Shaanxi Yanchuan Qiankunwan Scenic Area Cableway Project
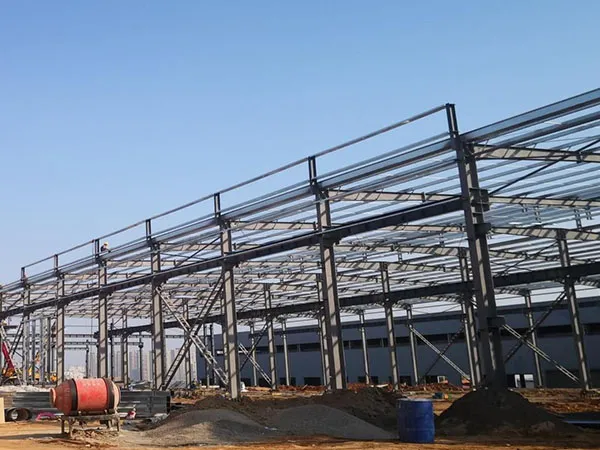

Luoyang Xuke Steel Structure Engineering
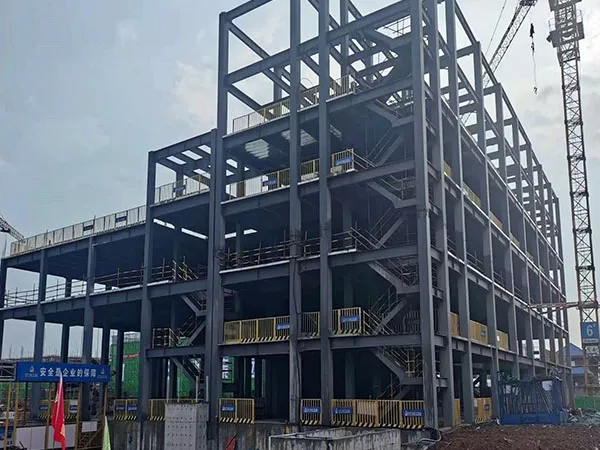

Luoyang Cold Chain Logistics Project